By dominating 41 this important Excel formula, You will get increased effectiveness and accuracy of results in your work. Using Excel formulas correctly can avoid mistakes and thus increase productivity in your work.
If you work with Excel without using formulas, The results obtained can be predicted not to be optimal. The formula function in Excel provides great benefits in calculating, analyze, and present data efficiently. By using the formula, you can do mathematical calculations, statistics, logic, and much more easily and accurately. Also learn step by step how to create a formula in Excel.
In using Excel formulas, You can use Excel's built-in functions or a combination of several functions. Below are some important Excel formula functions for work and examples of their use.
List of contents
Excel Formula Functions by Category
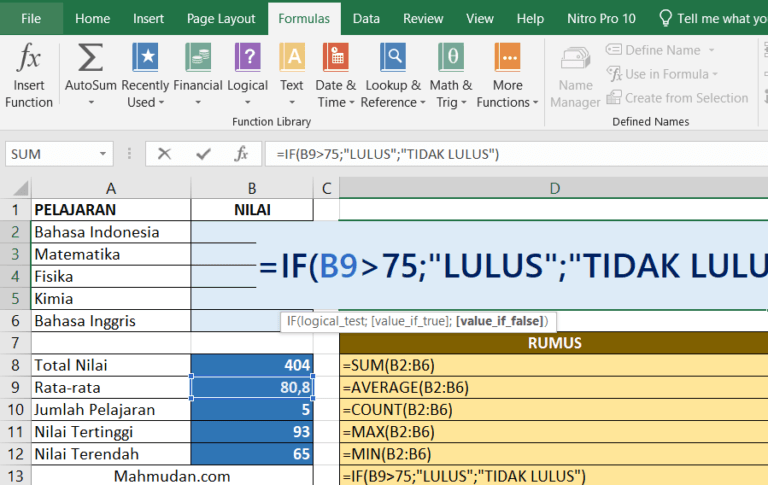
Every formula written in Excel always begins with an equal sign (” = “).
Mathematical Functions
- SUM Adds a range of numbers. Sample: =SUM(A1:A5)
- MAX Returns the highest value in a number range. Sample: =MAX(A1:A5)
- MIN Returns the lowest value in a number range. Sample: =MIN(A1:A5)
- ROUND Rounds a number to a specific number of digits. Sample: =ROUND(A1;2)
- ROUNDUP Rounds a number up to a specified number of digits Example: =ROUNDUP(A1;2)
- ROUNDDOWN Rounds a number down to a specified number of digits. Sample: =ROUNDDOWN(A1;2)
- RAND Returns an intermediate random number 0 And 1. Sample: =RAND()
- SUMIF Sums cells in a range that meet certain criteria. Sample: =SUMIF(A1:A5;”>10″)
- SUMIFS Sums cells in a range that meet certain criteria. Sample: =SUMIFS(A1:A5,”>10″,B1:B5,”<20″)
Statistical Functions
- AVERAGE Calculates the average of a range of numbers. Sample: =AVERAGE(A1:A5)
- COUNT Counts the number of cells in a range that contain numbers. Sample: =COUNT(A1:A5)
- COUNTIF Counts the number of cells in a range that meet certain criteria. Sample: =COUNTIF(A1:A5;”>10″)
- AVERAGEIF Calculates the average of cells in a range that meet certain criteria. Sample: =AVERAGEIF(A1:A5;”>10″)
- COUNTIFS Counts the number of cells in a range that meet some specified criteria. Sample: =COUNTIFS(A1:A5;”>10″,B1:B5;”<20″)
- RANK Returns the rank of a number in a number range; Sample: =RANK(A1;A2:A5)
- AVERAGEIFS Calculates the average of cells in a range that meet certain criteria. Sample: =AVERAGEIFS(A1:A5,”>10″,B1:B5;”<20″)
Logical Functions
- IF Returns one value if a condition is true and another value if it is false. Sample: =IF(A1>10;”Yes”;”No”)
- AND Returns TRUE if all arguments are true. Sample: =AND(A1>10;BI<20)
- OR Returns TRUE if any argument is true. Sample: = OR(A1>10;BI<20)
- NOT Returns the inverse of a logical value. Sample: =NOT(A1>10)
- IFERROR Returns a value if the formula evaluates to error: if not, returns the formula result; Sample: =IFERROR(A1/b1;”Error”)
Date And Time Function
- TODAY Returns the current date. Sample: =TODAY()
- NOW Returns the current date and time. Sample: =NOW()
- DATE Returns the date serial number . Sample: =DATE(2022;4;6)
- TIME Returns the time serial number. Sample: =TIME(12;30;0)
Search and Reference Function
- VLOOKUP Looks up a value in a table and returns the corresponding value in the same row Example: =VLOOKUP(A1;A2:B5;2;FALSE)
- Hlookup Looks up a value in a table and returns the corresponding value in the same column Example: = Hlookup(A1;A2:B5;2;FALSE)
- INDEX Returns a value or reference to a value from within a table or range Example: =INDEX(A1:B5;3;2)
- MATCH Searches for a value in a range and returns the position of the value in that range Example: =MATCH(A1;A2:A5;0)
- CHOOSE Selects a value from a list of values based on a specified position Example: =CHOOSE(2;”Monday”;”Tuesday”;”Wednesday”)
Text Functions
- CONCAT Combines two or more text strings into one string. Sample: =CONCATENATE(“Hello”;””;”World”)
- LEFT Returns the specified number of characters from the left of the text string. Sample: =LEFT(A1;5)
- RIGHT Returns the specified number of characters from the right of the text string. Sample: =RIGHT(A1;5)
- MID Returns the specified number of characters from the middle of the Example text string: =MID(A1;3;5)
- LEN Returns the length of the text string. Sample: =LEN(A1)
- SUBSTITUTE Replaces text in a text string with new text. Sample: =SUBSTITUTE(A1;”old”;”new”)
- TRIM Removes leading and trailing spaces from a text string. Sample: =TRIM(A1)
- PROPER Relating the first letter of each word in the text string. Sample: =PROPER(A1)
- LOWER Converts all letters in text to lowercase. Sample: =LOWER(A1)
- UPPER Converts all letters in text to uppercase. Sample: =UPPER(A1)
- TEXT Converts a value to text in a specific format. Sample: =TEXT(A1;”0;00″)
Combining Functions in Excel Formulas
On Microsoft Excel, You can create a formula using a combination of several functions such as a combination of basic mathematical operations, namely summation, subtraction and multiplication. Sample:
Added and less formulas:
=SUM(A1:A5)-(B1+C3+D6)
Besides that, You can also create more complex formulas by combining several other functions like the example below:
Formula for Calculating Age:
=CONCATENATE(DATEDIF(A1;NOW();”Y”);” Year “;DATEDIF(A1;NOW();”YM”);” Month “;DATEDIF(A1;NOW();”MD”);” Day”)
That is 41 Excel formulas are important and most widely used in the field of office work.
Hope it is useful.